Last updated [2025.6.12]
1. Introduction
Before we dive into CRUD optimization, let’s first define CRUD and its importance in software development. Understanding these basics is crucial, especially for new developers.

1.1 What is CRUD?
CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, and Delete —the fundamental operations of persistent storage systems. Nearly every database-driven application requires these operations:
- Create: Inserting new records into the database.
- Read: Retrieving and viewing data from the database.
- Update: Modifying existing records in the database.
- Delete: Removing records that are no longer needed.
🙌 Try it out:Chapter 3: Task Data Management
1.2 The Importance of CRUD in Software Development
- Data Management Foundation: CRUD operations form the backbone of any data-driven application. Whether you’re managing a simple to-do list or a complex enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, these basic operations are essential for data management.
- Key to User Interaction: Most user interactions with applications boil down to these four operations. For example, in social media apps, posting content (Create), Browse the feed (Read), editing profiles (Update), and deleting comments (Delete) are all CRUD operations in action.
- Foundation of System Design: When designing software systems, CRUD operations are often the starting point for discussions and planning. They help developers clarify data models and business logic.
- Focus of Performance Optimization: Because CRUD operations are so frequent, their efficiency directly impacts overall application performance. Therefore, optimizing CRUD operations is crucial for improving system performance.
💡 Read More: How to Design an RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) System
1.3 Typical Implementation of CRUD
CRUD operations are implemented in various ways across different technology stacks, but the underlying principles remain consistent. Here are common examples:
- SQL Databases:
- Create:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2) VALUES (value1, value2); - Read:
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE condition; - Update:
UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1 WHERE condition; - Delete:
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;
- Create:
- RESTful APIs:
- Create: HTTP POST request
- Read: HTTP GET request
- Update: HTTP PUT or PATCH request
- Delete: HTTP DELETE request
- ORM (Object-Relational Mapping): Many programming languages and frameworks provide ORM tools that abstract database operations into object manipulations, simplifying CRUD implementation.
Teams that can quickly build, iterate, and deploy applications often gain a competitive edge. Thus, optimizing CRUD operations is not just a technical task, but a strategic decision that directly impacts business success.
This article will explore how to significantly boost development efficiency by optimizing CRUD operations. We’ll delve into common pain points in traditional CRUD development, explore code generation tools, and introduce revolutionary low-code platform solutions.
Whether you are an experienced developer or new to programming, this article will provide valuable insights and practical strategies to help you achieve greater efficiency in CRUD development.
2. Pain Points in Traditional CRUD Development
While CRUD operations are central to most applications, traditional CRUD development methods often come with a series of frustrating challenges:
- Repetitive Code Writing: Developers frequently write nearly identical CRUD code across projects. This is time-consuming and error-prone.
- Time-Consuming Basic Functions: Essential CRUD functionality is necessary but rarely the core value of an application. Yet, development teams often spend significant time on these basics, leaving less time for unique business logic and user experience.
- Difficulty Adapting to Changing Requirements: In traditional development, modifying CRUD operations to meet evolving business needs can require extensive code refactoring, reducing development flexibility.
- Challenges of Cross-Platform Development: With the rise of mobile and web applications, developers must write and maintain multiple sets of CRUD code for different platforms, increasing workload and complexity.
- Consistency and Standardization Issues: In large projects or teams, different developers might implement CRUD operations in various ways, making the codebase difficult to maintain and extend.
- Performance Optimization Challenges: While basic CRUD operations are easy to implement, ensuring efficient performance at scale, especially under high concurrency, often requires complex optimizations. Additionally, ensuring seamless collaboration and feedback management is a common challenge in CRUD development. Developers often struggle with gathering and implementing feedback efficiently, leading to delays and miscommunication. A website proofing tool can simplify this process by allowing clients and team members to provide direct, contextual feedback within the application, reducing back-and-forth and streamlining issue resolution.
- Security Concerns: Each CRUD operation can be a potential security vulnerability. Ensuring proper security for each operation is a burdensome and error-prone task.
Recognizing these pain points is the first step in optimizing the CRUD development process. Next, we will explore modern solutions that effectively address these issues and significantly improve development efficiency.
3. The Role of Code Generation Tools
In response to the many challenges of traditional CRUD development, code generation tools have emerged as powerful allies in improving development efficiency. These tools can automatically generate standardized CRUD code, significantly reducing repetitive tasks and allowing developers to focus more on core business logic.
💡 Read More:Top 8 Open-Source CRUD Projects with the Most GitHub Stars
3.1 Common CRUD Code Generation Tools
-
Swagger Codegen: Automatically generates client SDKs, server stubs, and API documentation based on the OpenAPI specification.
-
JHipster: A development platform for generating, developing, and deploying full-stack web applications based on Spring Boot and front-end frameworks like Angular, React, or Vue.
-
MyBatis Generator: Generates Java POJO objects, XML mapping files, and CRUD operation code for the MyBatis framework.

-
Entity Framework Power Tools: A database reverse engineering tool for .NET development, generating code and view models based on Entity Framework.
3.2 Advantages of Using Code Generation Tools
Code generation tools not only help developers save significant time but also ensure code quality and consistency. Their advantages are primarily reflected in the following aspects:
- Increased Development Speed: Automatically generating basic CRUD code saves substantial development time.
- Error Reduction: Generated code is often thoroughly tested, reducing human errors.
- Standardization: Ensures consistent CRUD implementation across the team.
- Ease of Maintenance: Generated code typically follows best practices, making it easier to maintain.
- Rapid Prototyping: Quickly generating functional prototypes accelerates development iterations.
3.3 Best Practices for Using Code Generation Tools
Effective use of these tools still requires following some best practices. Here are some recommendations to help developers maximize the potential of code generation tools in their projects:
- Choose the Right Tool: Select the most suitable code generation tool based on your project needs and team tech stack.
- Customize Generation Templates: Adjust code generation templates to meet specific project requirements and coding standards.
- Version Control: Include generated code in version control, distinguishing between automatically generated and manually modified parts.
- Continuous Integration: Integrate code generation into your CI/CD process to ensure generated code is always in sync with the data model.
- Combine with Manual Coding: Use the generated code as a starting point, then manually add specific business logic and custom features.
4. Revolutionizing CRUD Application with Low-Code Platforms
Beyond code generation tools, low-code platforms are revolutionizing CRUD development.
These platforms enable developers to rapidly build applications through graphical interfaces and pre-built components, significantly reducing the need for manual coding.
For CRUD operations, low-code platforms offer a transformative approach, making the creation, configuration, and deployment of data management applications easier than ever.
💡 Read More:Open Source CRUD Development Tools: NocoBase vs Refine
4.1 Low-Code Platforms: A Game-Changer for CRUD Apps
Take NocoBase as an example—a low-code/no-code platform that provides developers with flexible, powerful, and easy-to-use CRUD solutions.
💡 Dig deeper: NocoBase Transforms Education Management at University of Siena
Here’s how NocoBase simplifies the CRUD development process:
- Visual Data Model Design
- Define data structures through an intuitive graphical interface.
- Support complex relationships (one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many) with ease.
- Preview and modify data models in real-time.
- Automatic API and Management Interface Generation
- Automatically generate RESTful APIs based on defined data models.
- Create corresponding data management interfaces, including list, detail, creation, and editing pages.
- Support common filtering, sorting, and pagination features.
- Flexible Interface Customization
- Use a drag-and-drop interface builder to create custom page layouts effortlessly.
- Leverage a rich library of pre-built UI components to meet various display needs.
- Develop custom components to fulfill unique business requirements.
- Built-In Workflow Engine
- Visually define business processes with the built-in workflow engine.
- Seamlessly integrate CRUD operations with business workflows.
- Support complex conditional logic and automated actions.
4.2 Case Study: Building a Complete CRUD App with NocoBase
Let’s dive into a real-world example to see how NocoBase transforms the CRUD app development process.
Imagine you’re the tech lead at a mid-sized software company, tasked with building a project management system for a rapidly growing startup.
The traditional development approach would take at least two weeks, but the client needs a working prototype in just three days.
This is where NocoBase shines.
👀️ Project Requirements:
- Manage projects, tasks, and team members.
- Track task status and deadlines.
- Generate project progress reports.
- Implement role-based access control.
- Integrate simple workflow automation.
Let’s see how NocoBase can accomplish this seemingly impossible task in just a few hours.
1. Project Setup and Data Model Design (60 minutes)
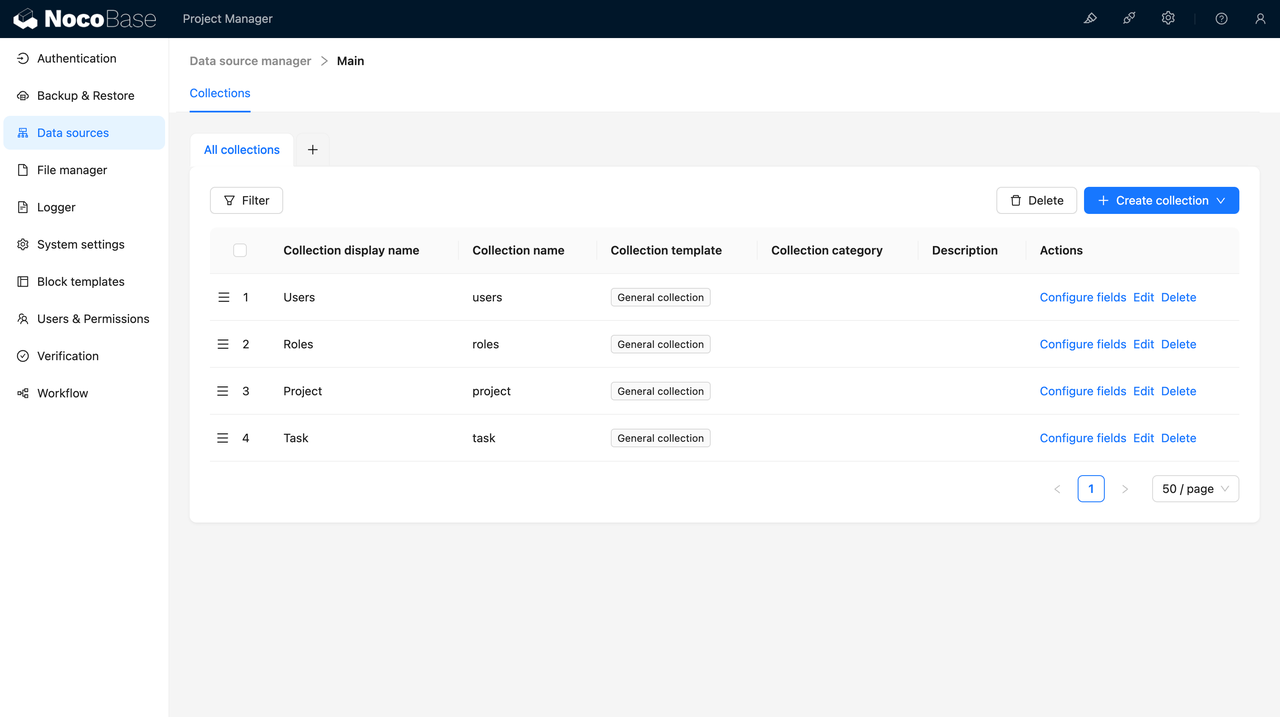
Log in to NocoBase and create a new project: “Project Manager.”
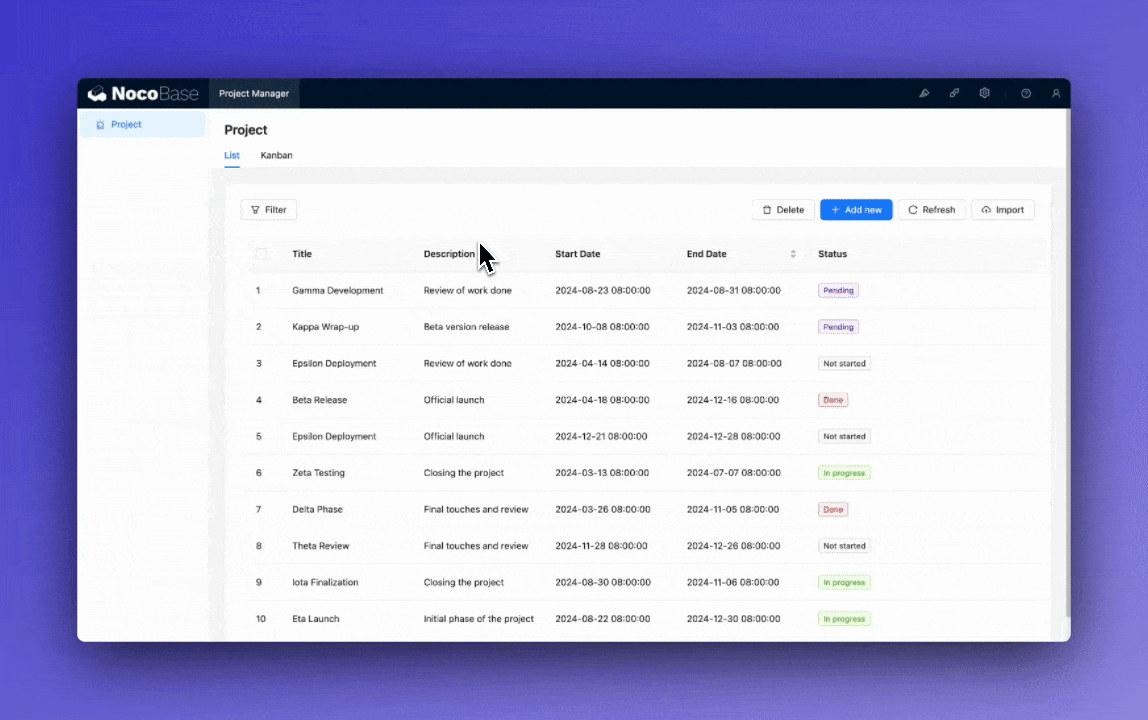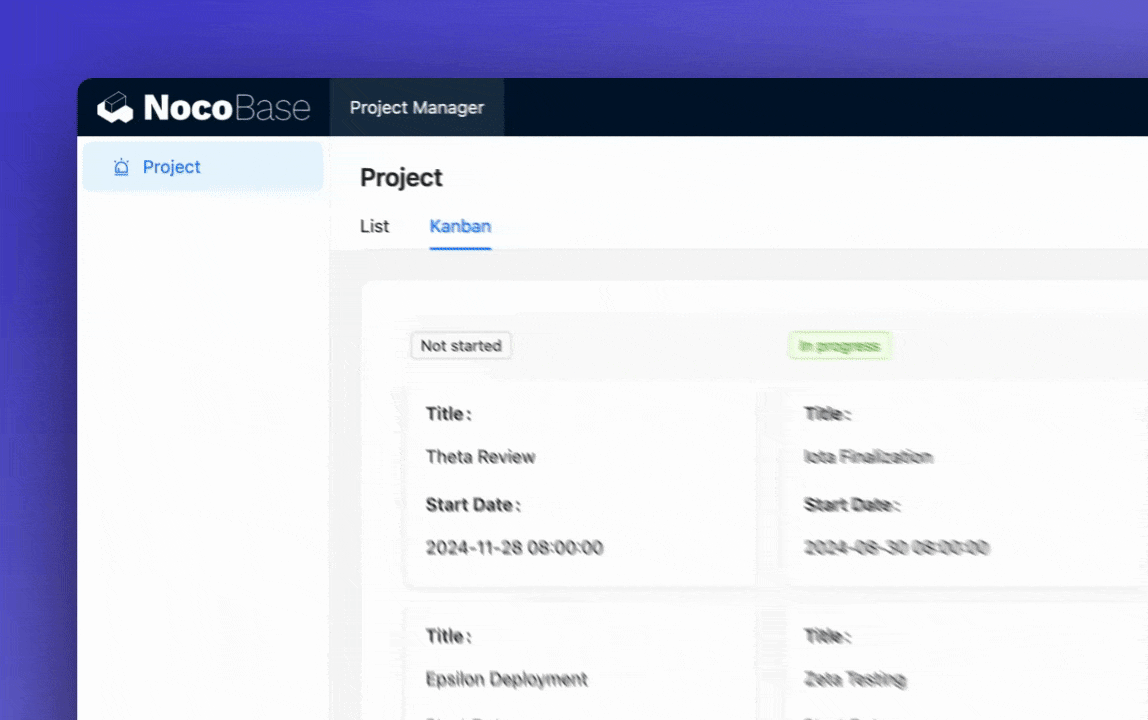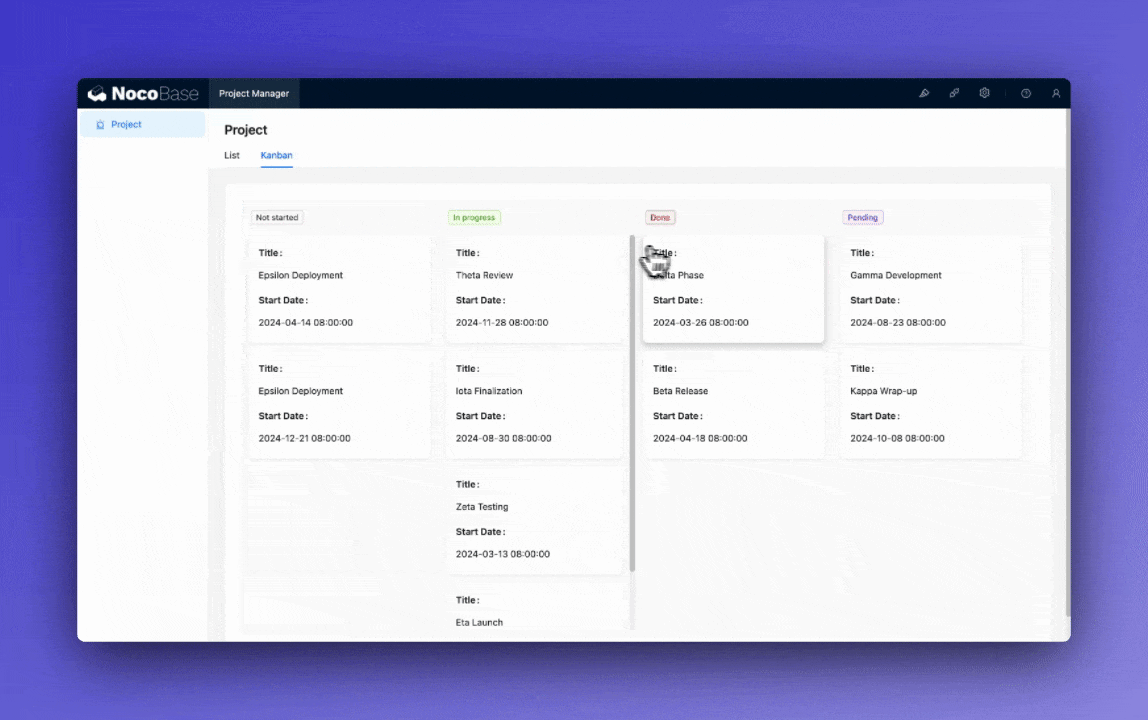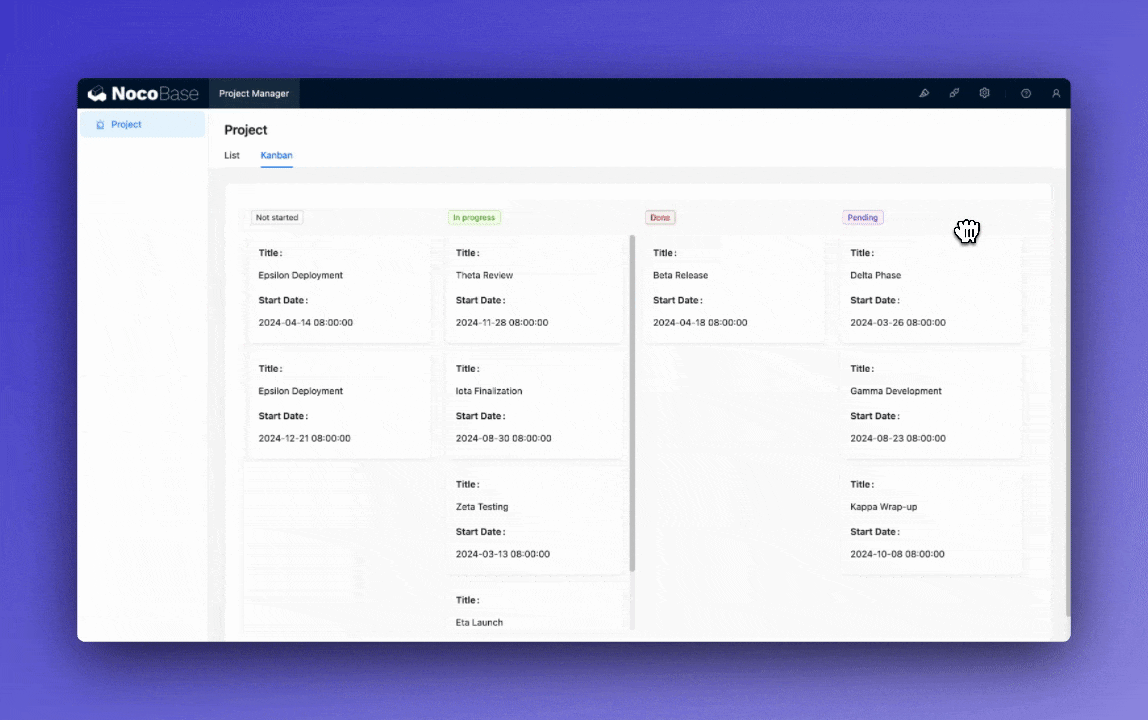
Use the visual interface to create the following data models:
- Project: Title, Description, Start Date, End Date, Status, Budget
- Task: Title, Description, Due Date, Status, Priority
- User: Name, Email, Role
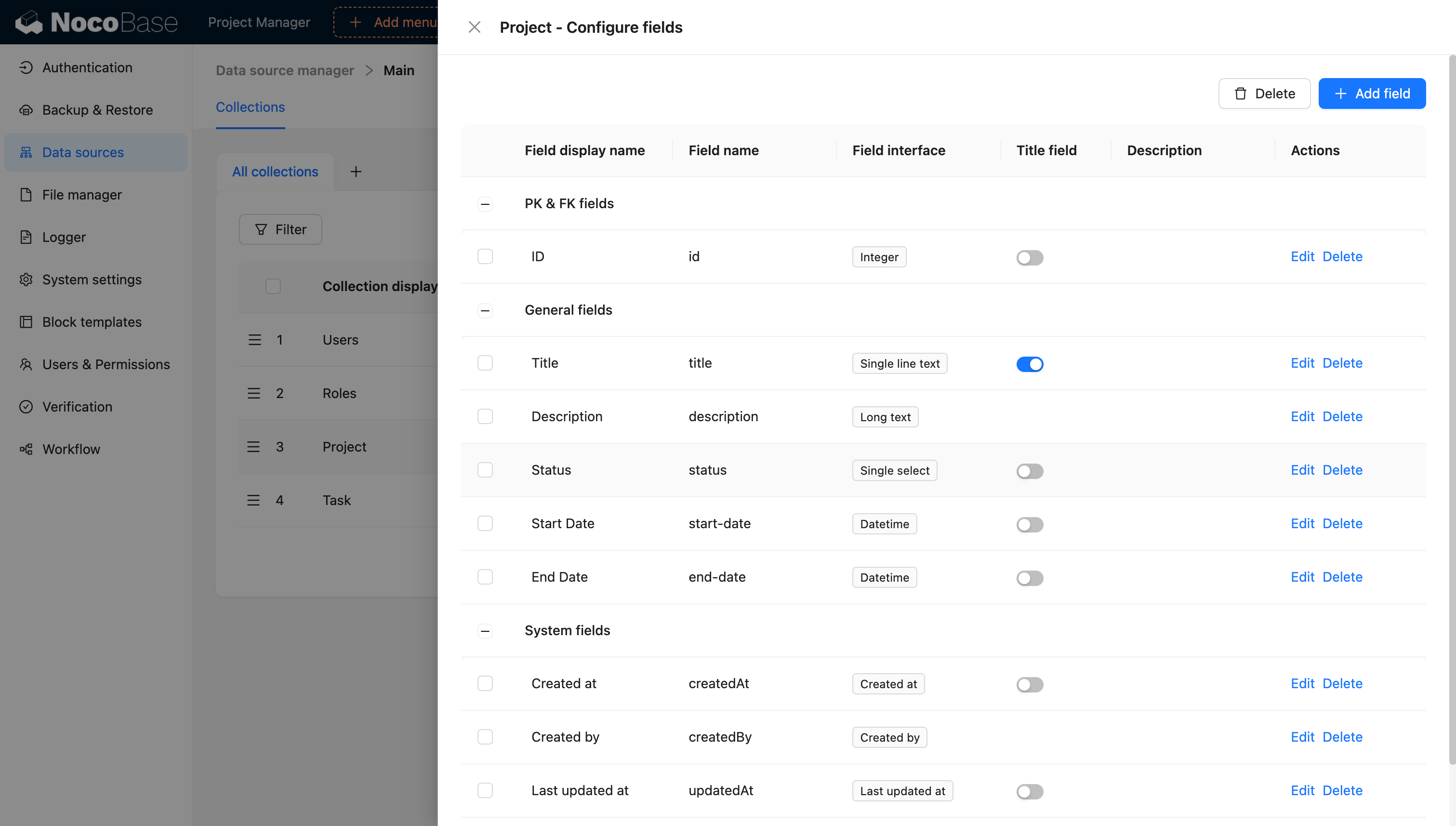
Set up relationships:
- Project 1-to-N Task
- User N-to-M Project (team members)
- User 1-to-N Task (assignee)
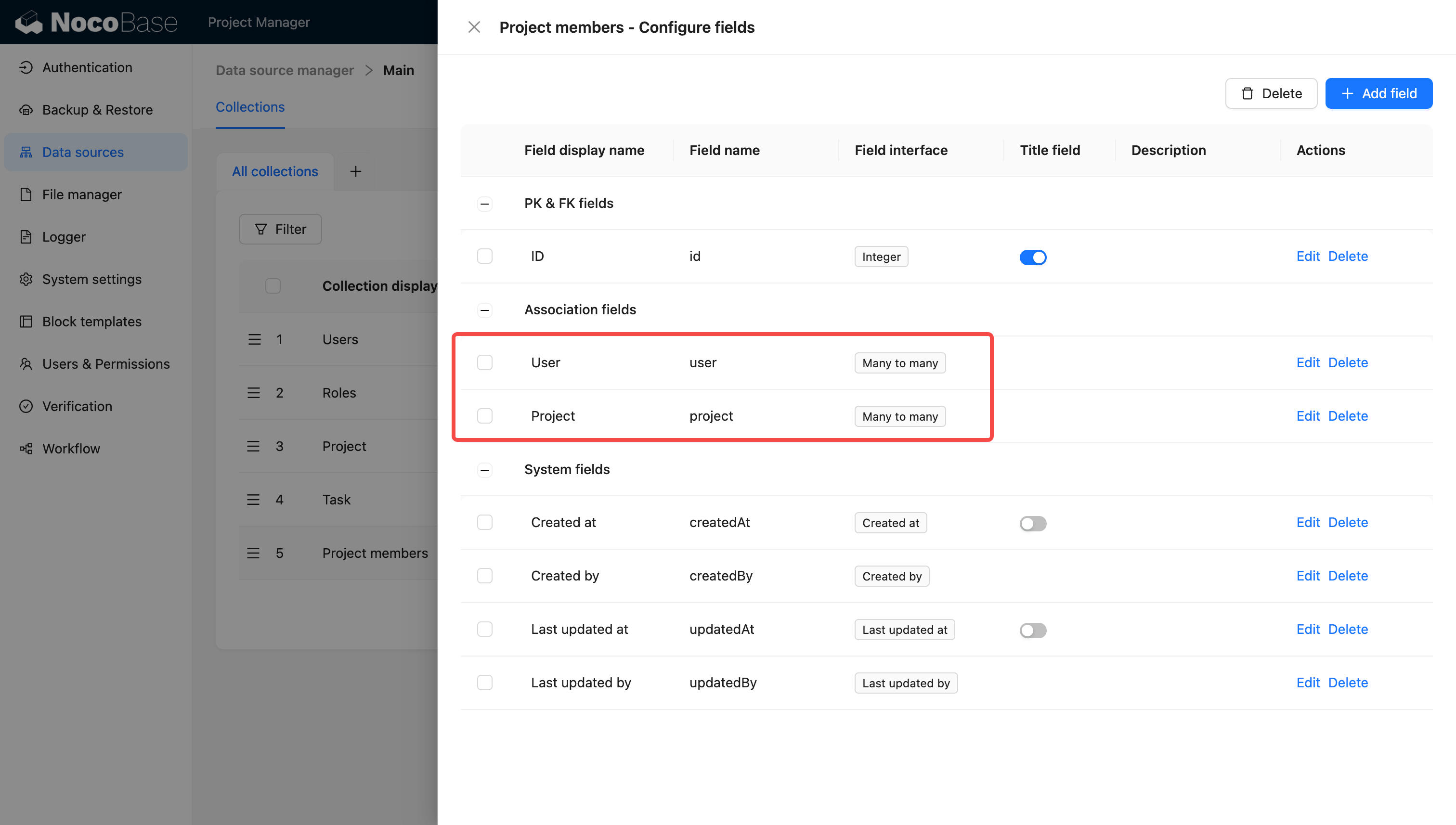
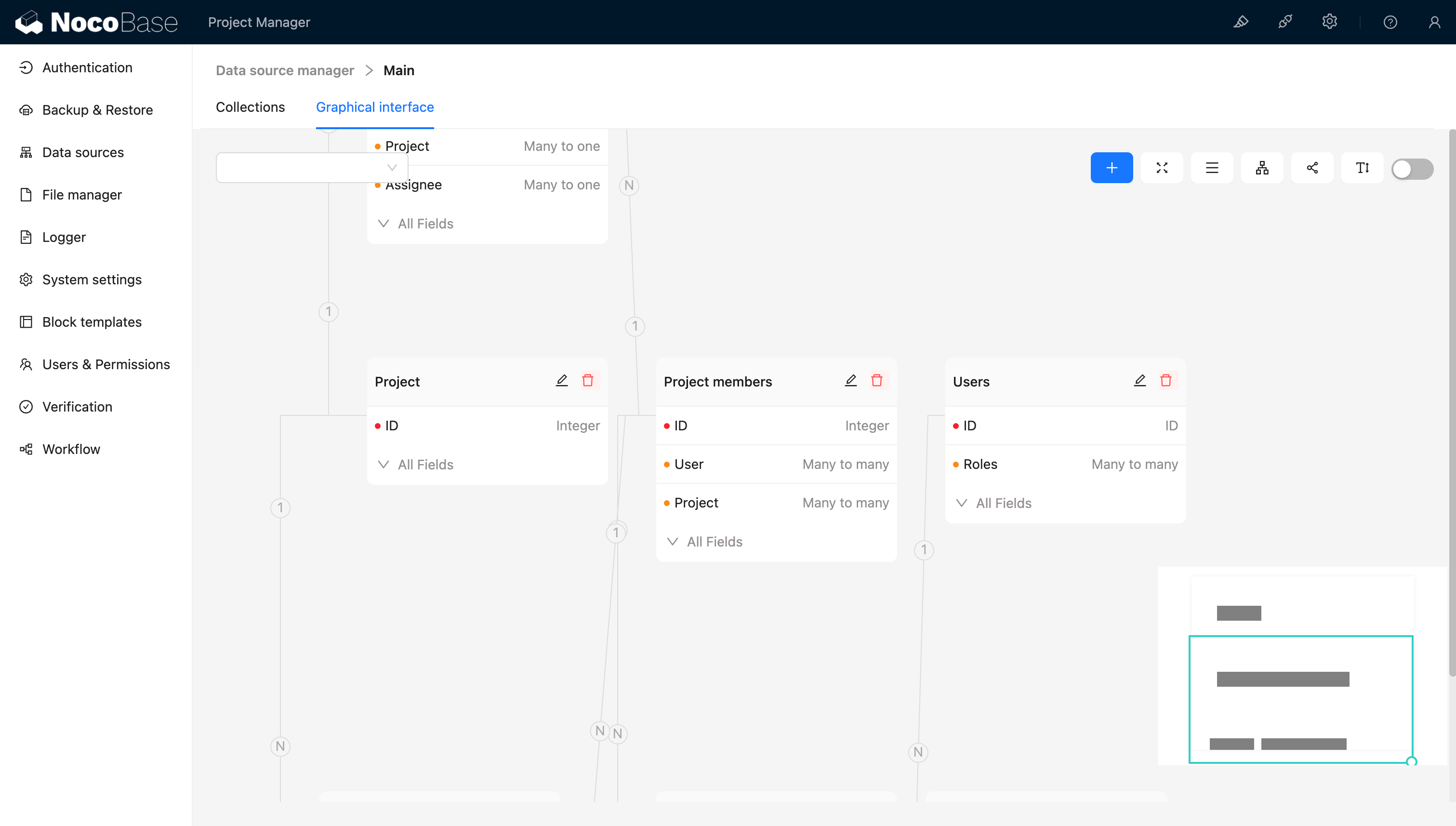
😕 Challenge: The client suddenly requested a “Budget” field for the project model.
👍 Solution: Using NocoBase’s instant field addition feature, this was done without redeployment.
2. Automatic CRUD Function Generation (15 minutes)
NocoBase automatically generates complete CRUD APIs and management interfaces for each data model.
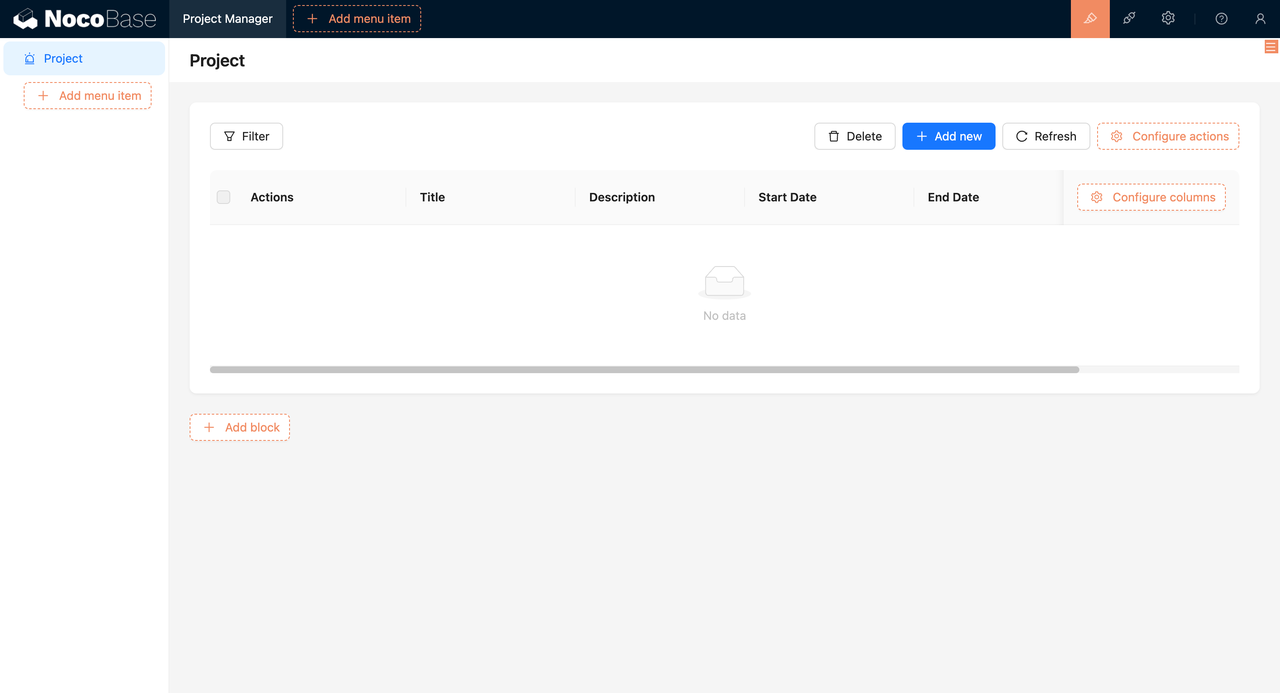
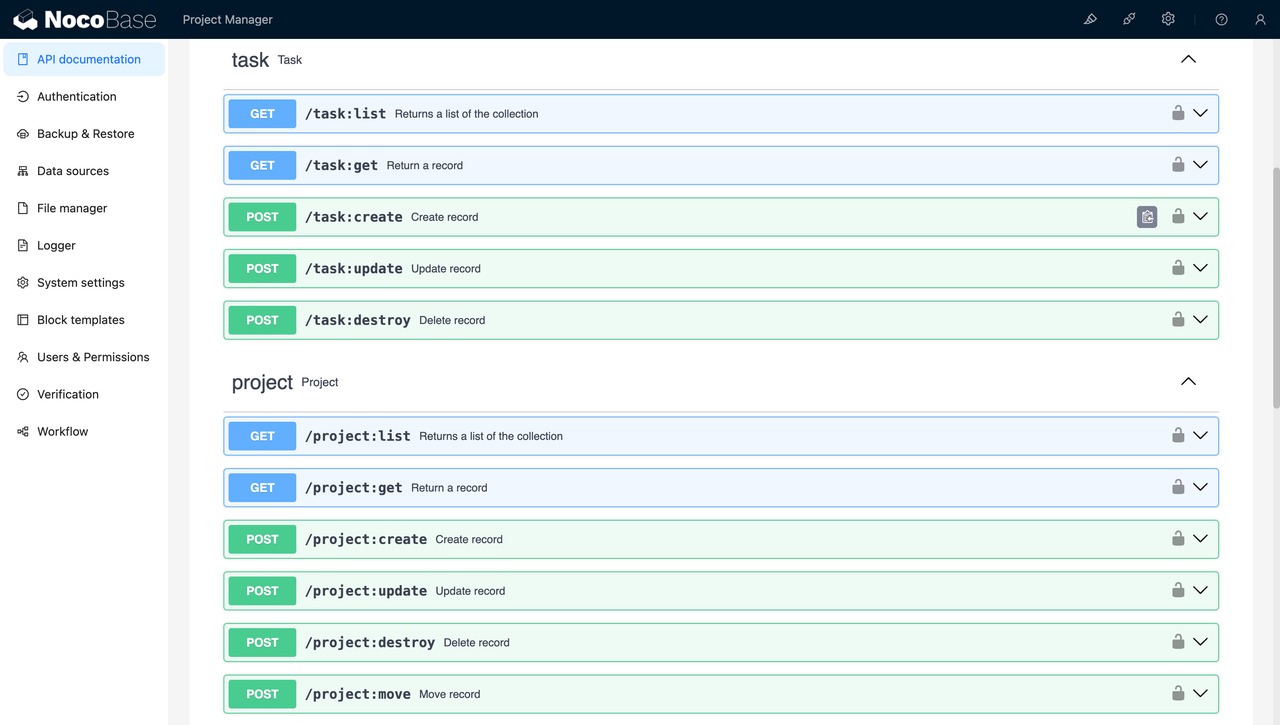
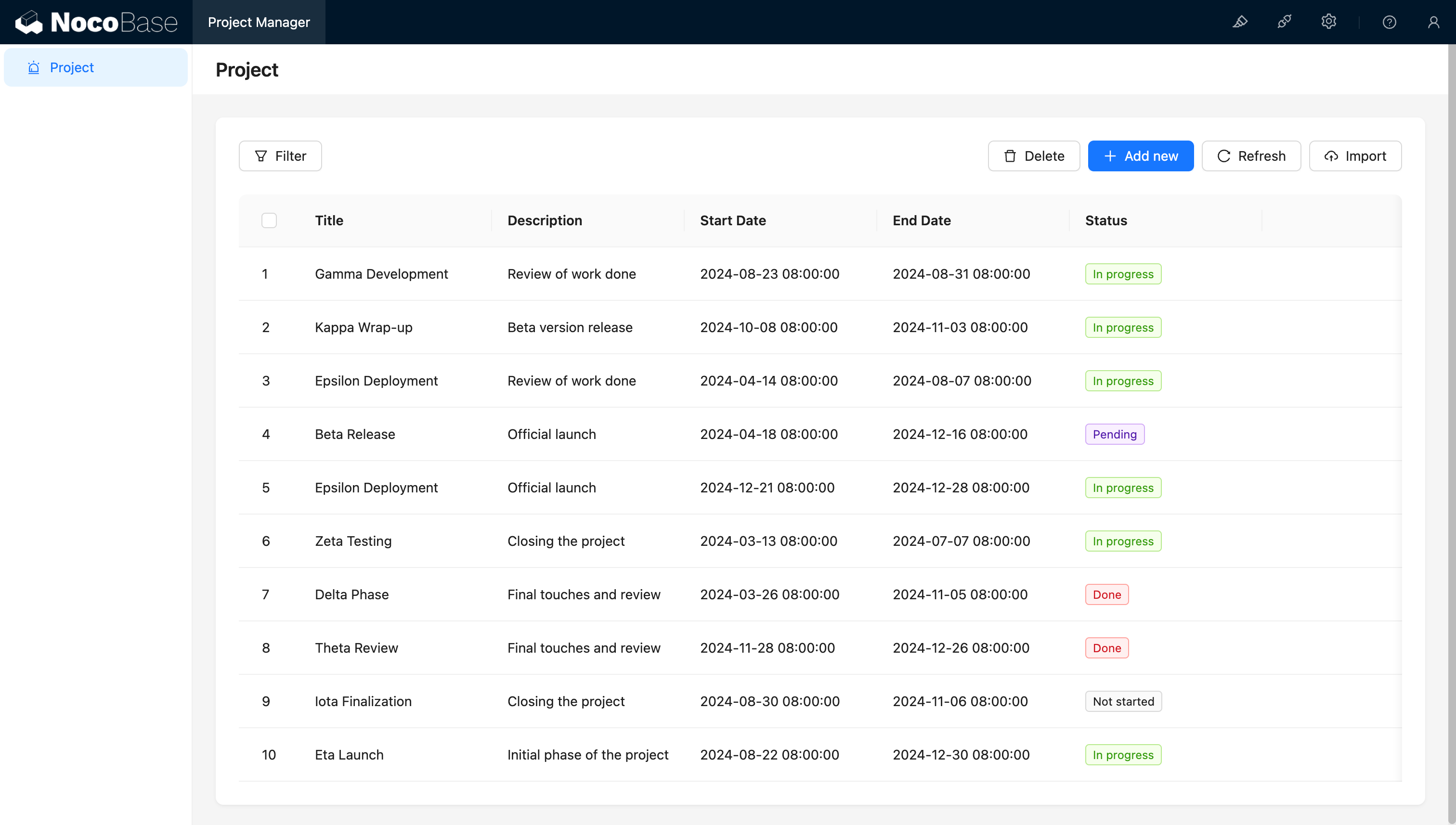
❤️ Unexpected Benefit: NocoBase automatically handled field validation and error processing, saving significant coding time.
3. Customizing List Views (45 minutes)
Add filters to the project list (by status and date range).
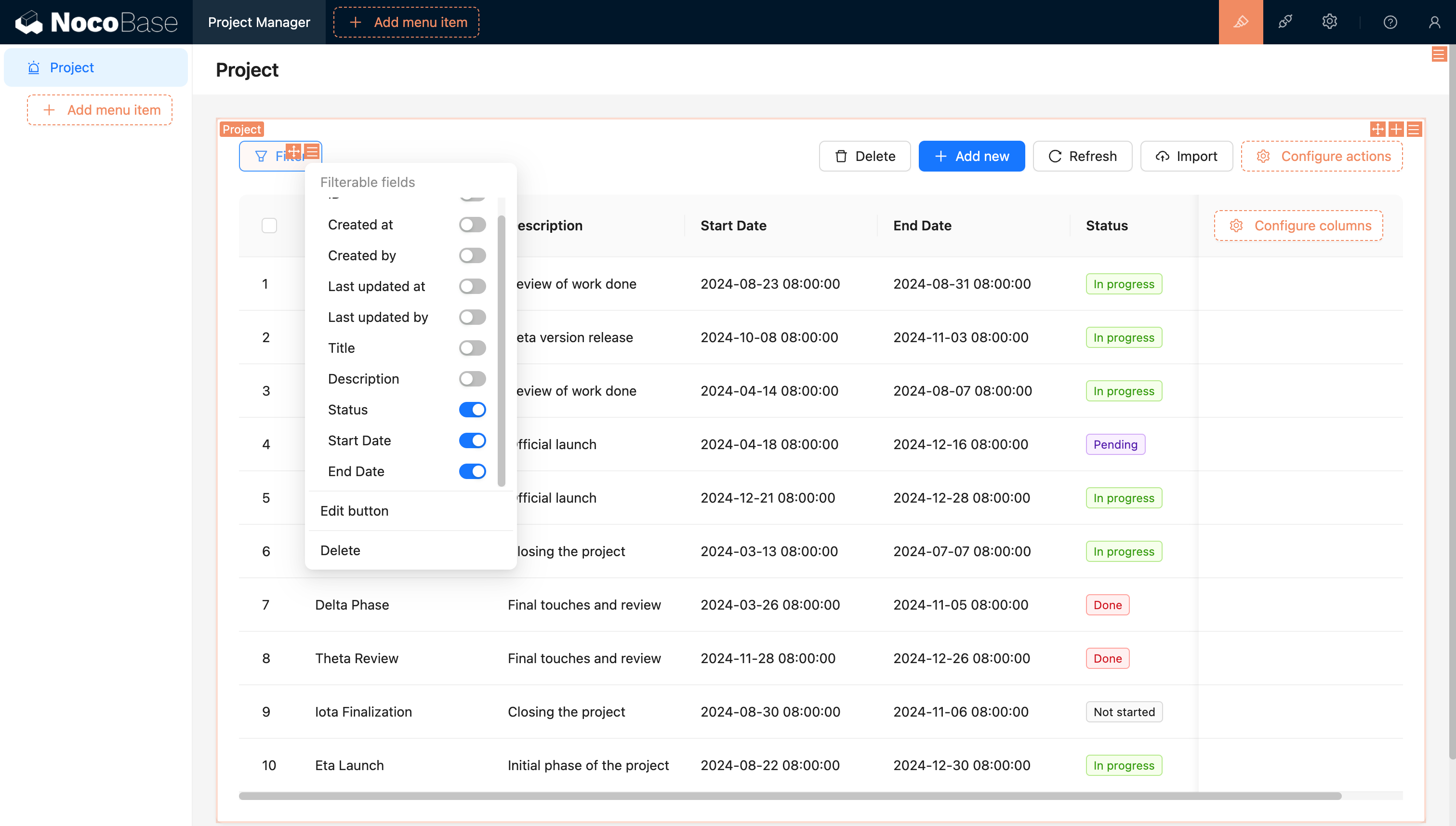
Add sorting options to the task list (by priority and due date).
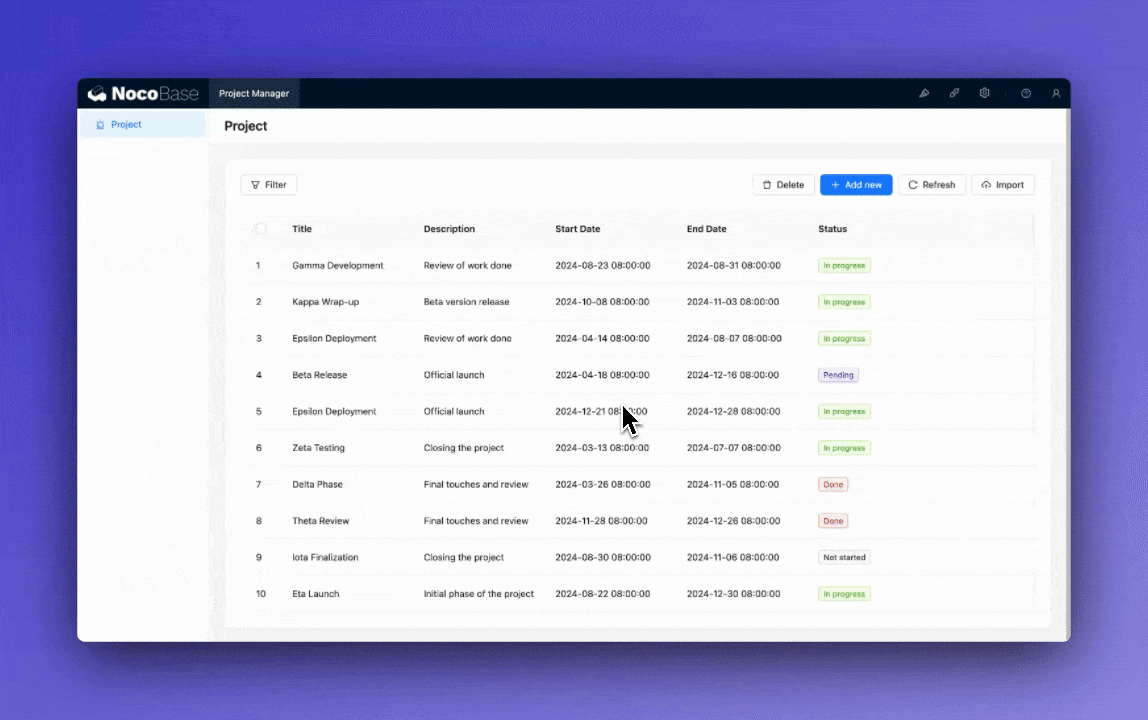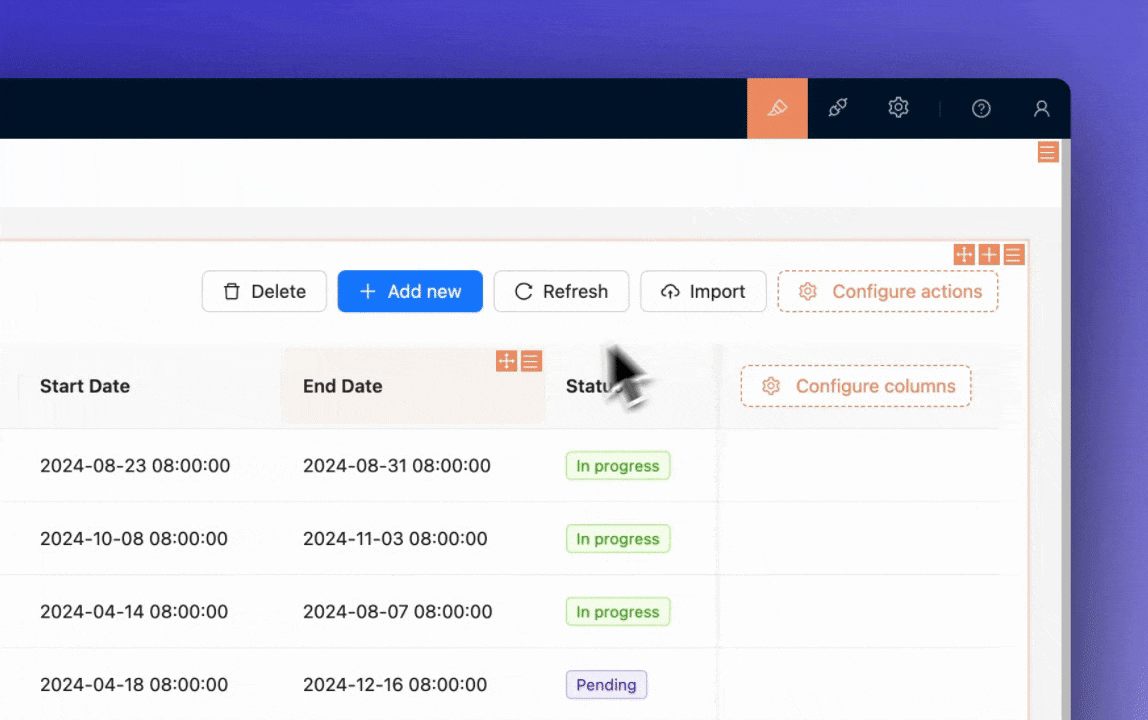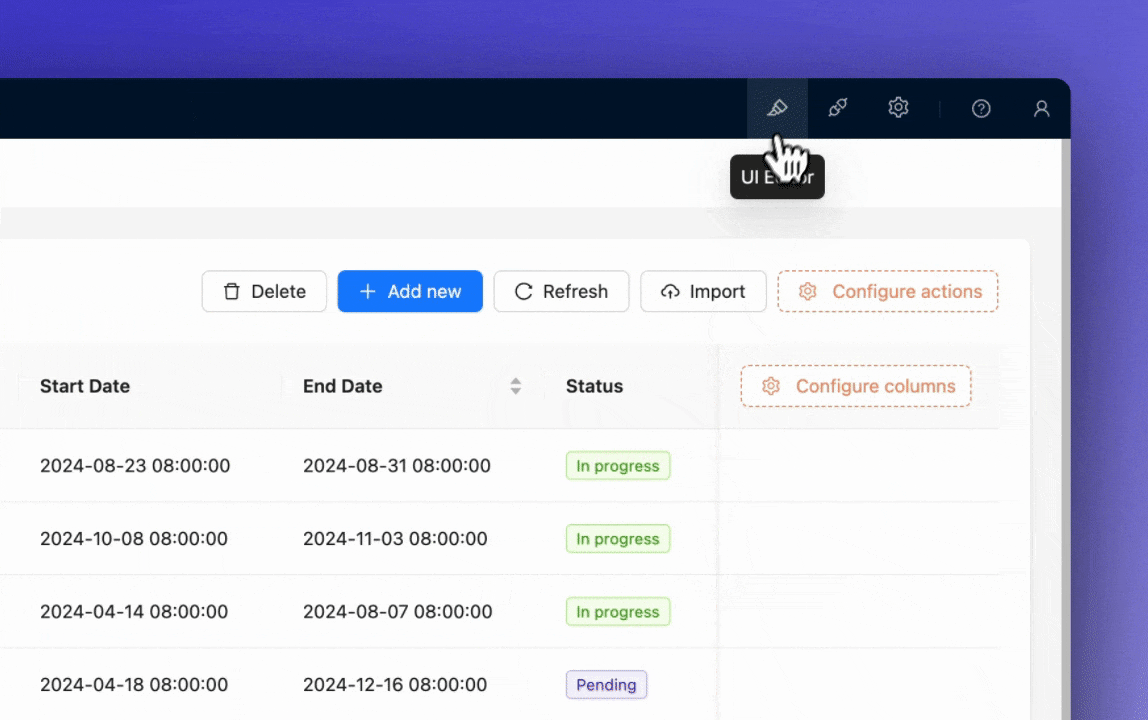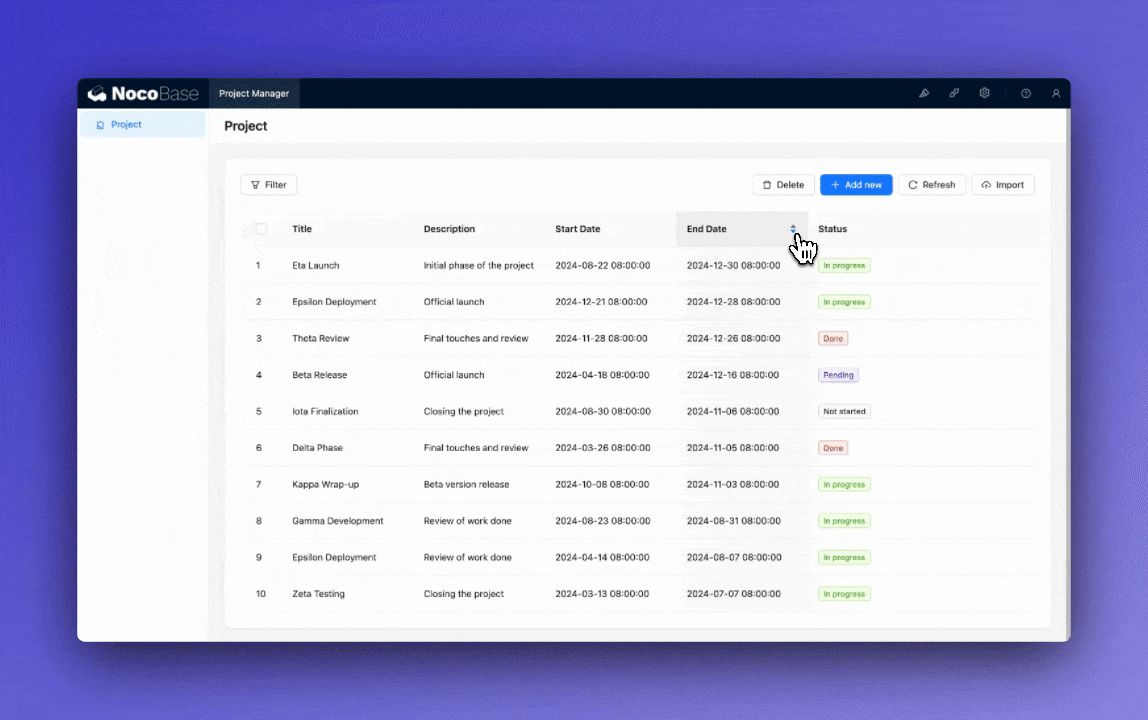
Customize the task board view to enable drag-and-drop functionality for updating task status.
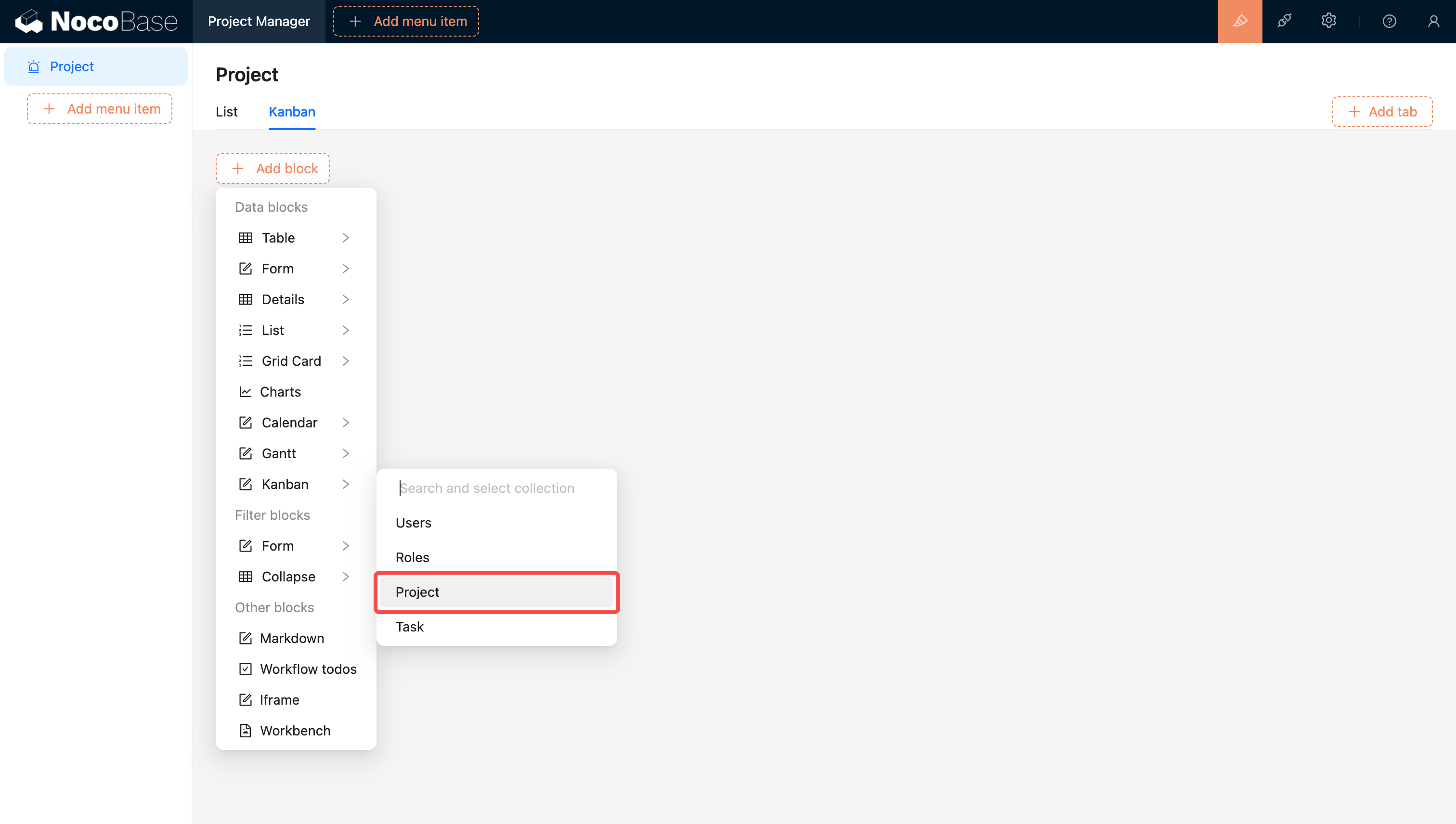
🎉️ Tip: Use NocoBase’s template feature to quickly copy and modify view configurations.
4. Dashboard Design (60 minutes)
Create an overview dashboard with:
- Project progress charts (using NocoBase’s built-in chart components).
- Upcoming task list.
- Team member workload statistics.
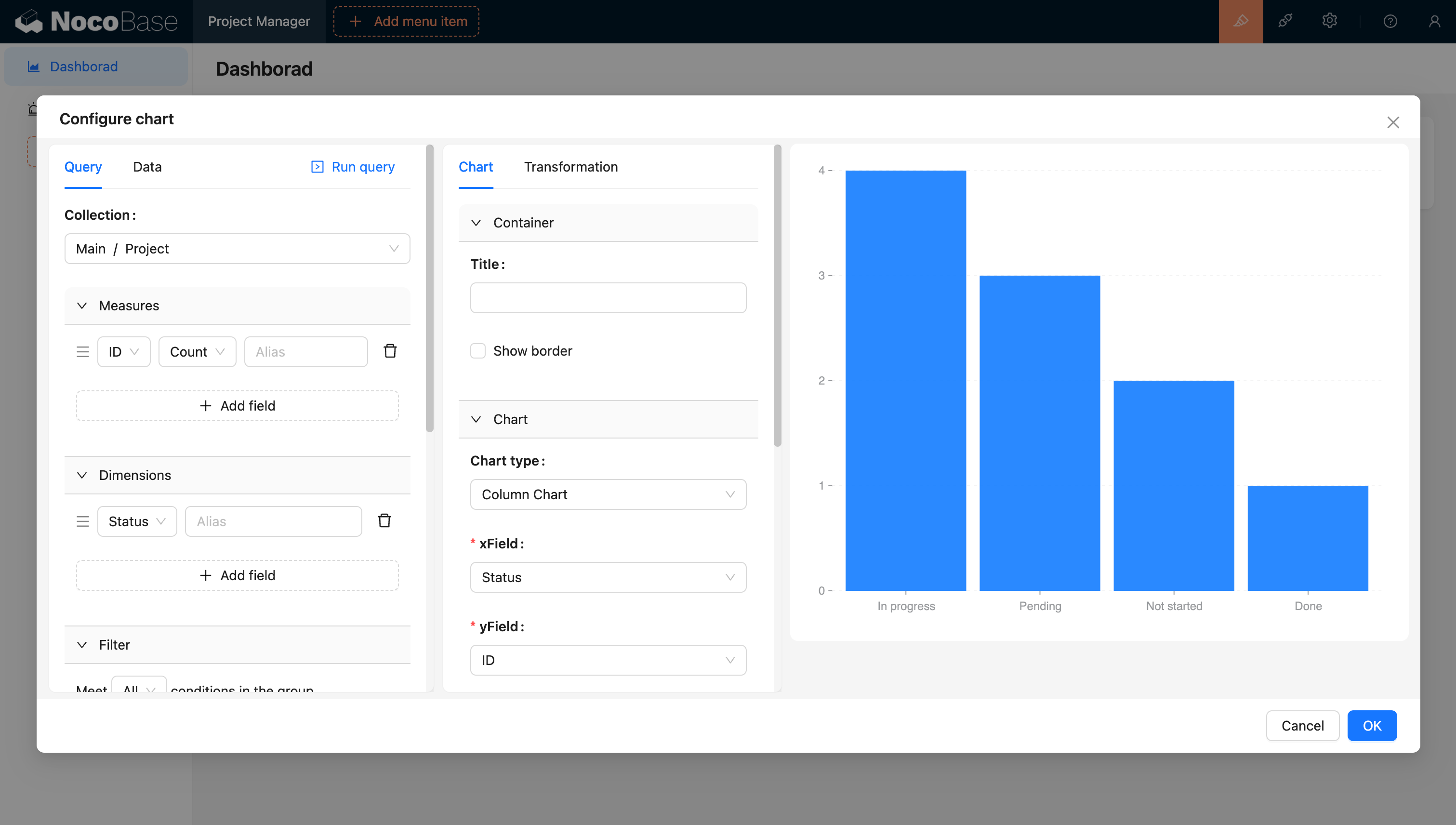
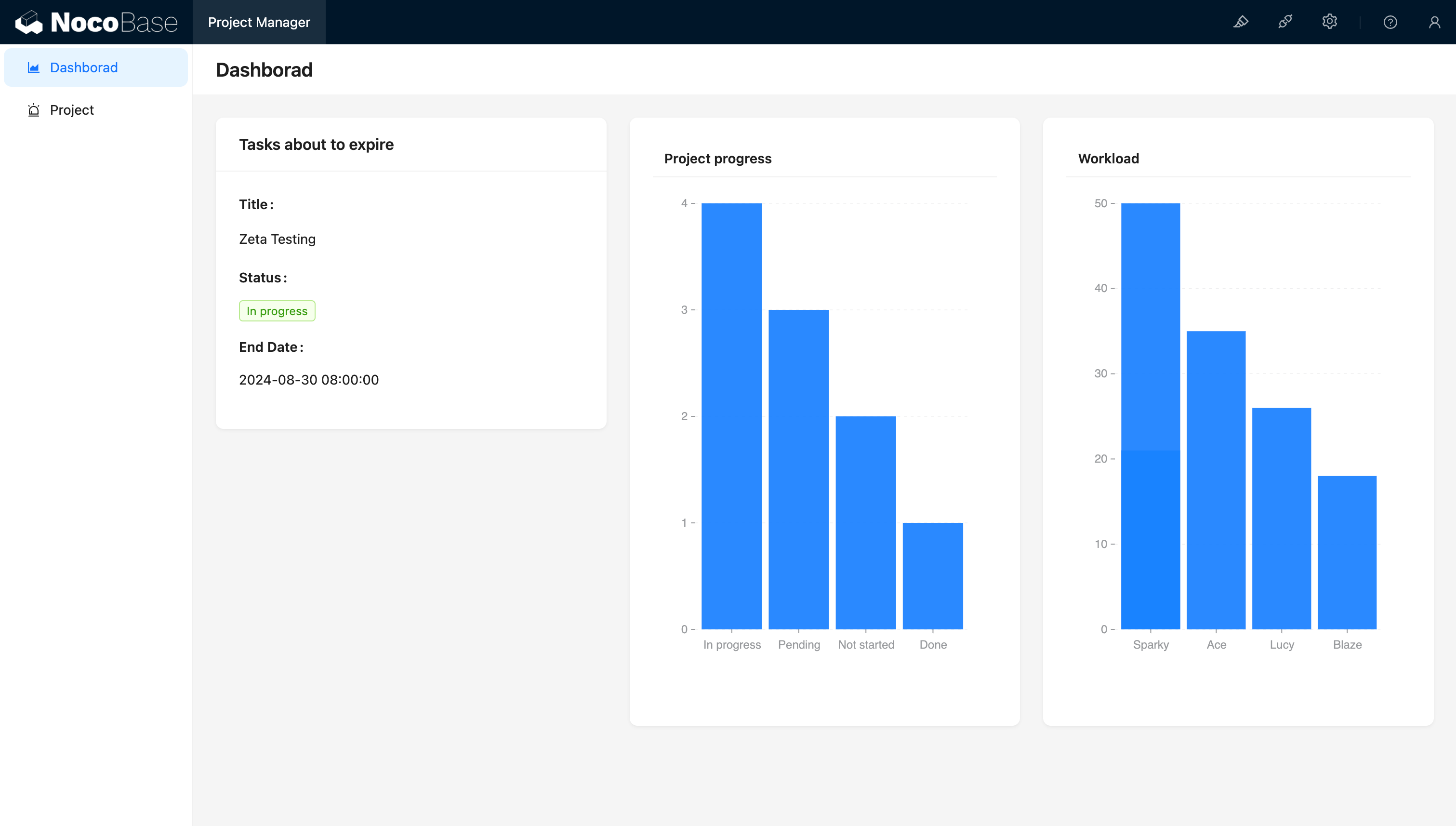
Using traditional development methods, a similar system might take days or even weeks to develop. But with NocoBase, we completed a fully functional CRUD app in just 2 hours. This not only dramatically increased development efficiency but also ensured the application’s quality and consistency.
💡 More Tutorials: Tutorials - NocoBase
Through this case study, we can see how low-code platforms like NocoBase are revolutionizing CRUD app development. They not only solve many of the pain points in traditional CRUD development but also provide developers with more room for innovation, allowing them to turn ideas into reality faster.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the significant impact of CRUD optimization on development efficiency. Starting from the pain points in traditional CRUD development, we introduced modern solutions such as code generation tools and low-code platforms, and discussed standardization and best practices for CRUD operations.
Comprehensive Impact of CRUD Optimization on Development Efficiency
- Time Savings: By using code generation tools and low-code platforms like NocoBase, developers can reduce CRUD development time by 50% or more.
- Error Reduction: Automation tools and standardized practices significantly reduce human errors, improving code quality.
- Increased Flexibility: Low-code platforms allow for quick adjustments and iterations, making applications more adaptable to changing needs.
- Focus on Core Business: Reducing time spent on basic CRUD operations allows developers to focus more on core business logic and user experience.
- Improved Collaboration Efficiency: Standardized CRUD practices and clear code structures enhance team collaboration.
We encourage developers and teams to actively experiment with new CRUD development tools and methods, especially innovative low-code platforms like NocoBase.
These tools not only enhance development efficiency but also inspire innovative thinking, helping teams explore new possibilities. Developers can choose a small project or a module of an existing project to try out new tools and collect feedback from team members during the trial, continuously adjusting and optimizing usage strategies.
💡 Dig deeper: Top 15 Open-Source Low-Code Projects with the Most GitHub Stars
By continuously optimizing the CRUD development process, we can not only improve development efficiency but also create better software products for users. In today’s rapidly advancing technological landscape, maintaining an open and innovative mindset and daring to try new tools and methods will be key to staying competitive.
References
For developers interested in further exploring CRUD optimization and related technologies, here are some valuable resources:
Tools and Platforms:
Articles and Tutorials:
- Clean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software Craftsmanship - by Robert C. Martin
- Domain-Driven Design: Tackling Complexity in the Heart of Software - by Eric Evans
Online Courses:
Related reading:
- Top 8 Open-Source CRUD Projects with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 5 Success Cases of Low-Code Open-Source Platforms
- 5 Challenges of Developing with a No-Code Platform
- The Top 12 Open-Source No-Code Tools with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 11 Open Source Internal Tools with the Most GitHub Stars
- Exploring RAD: 5 Best Application Cases